Если честно, VMware мне больше нравится чем VirtualBox, но лицензию я не хочу покупать для домашнего использования. По этому, выбор пал на то, чтобы перейти с VMware Fusion на VirtualBox. Для этого дела, мне пришлось зарегистрироваться на официальном сайте, заполнить данные. Но сразу я скачать не смог, возникли трудности с ПО и мне нужно было обратиться в поддержку. Поддержка решала данный вопрос около недели, но все решилось и я смог загрузить DMG на свой мак.
Конвертация VMware virtual machine -> VirtualBox на MacOS
Для начала, заходим на официальный сайт и качаем утилиту под названием «ovftool».
Установить DMG на МасОС через CLI можно так:
Установка dmg пакетов через CLI (командную строку) в MacOS X
Монтирование dmg образов через CLI (командную строку) в MacOS X
При использовании мака, утилита установится по следующему пути:
/Applications/VMware\ OVF\ Tool/ovftoolЧтобы получить помощь, выполните:
$ /Applications/VMware\ OVF\ Tool/ovftool -h
Usage: ovftool [options] <source> [<target>]
where
<source>: Source URL locator to an OVF package, VMX file, or virtual machine in
vCenter or on ESX Server.
<target>: Target URL locator which specifies either a file location, or a
location in the vCenter inventory or on an ESX Server.
If <target> is not specified, information about the source is displayed to the
console.
Options:
--acceptAllEulas : Accept all end-user licenses agreements
without being prompted.
--allowAllExtraConfig : Whether we allow all the ExtraConfig
options. These options are a security risk
as they control low-level and potential
unsafe options on the VM.
--allowExtraConfig : Whether we allow ExtraConfig options. These
options are a security risk as they control
low-level and potential unsafe options on
the VM.
--annotation : Add annotation to vi, vmx, vapprun, vCloud,
OVF, and OVA source locators
--authdPortSource : Use this to override default vmware authd
port (902) when using a host as source.
--authdPortTarget : Use this to override default vmware authd
port (902) when using a host as target.
--chunkSize : Specifies the chunk size to use for files in
a generated OVF package. The default is not
to chunk. The chunk size without unit is
assumed to be in megabytes. Accepted units
are b, kb, mb, gb; e.g., 2gb or 100kb.
--compress : Compress the disks in an OVF package. Value
must be between 1 and 9. 1 is the fastest,
but gives the worst compression, whereas 9
is the slowest, but gives the best
compression.
--computerName : Sets the computer name in the guest for a VM
using the syntax --computerName:<VM
ID>=<value>. Only applies to vCloud targets
version 5.5 or newer.
--coresPerSocket : Specifies the distribution of the total
number of CPUs over a number of virtual
sockets using the syntax
--coresPerSocket:<VM ID>=<value>. Only
applies to vCloud targets version 5.5 or
newer.
-ds/--datastore : Target datastore name for a VI locator.
--decodeBase64 : Decode option values with Base64.
--defaultStorageProfile : The storage profile for all VMs in the OVF
package. The value should be an SPBM profile
ID. Only applies to VI targets version 5.5
or newer.
--defaultStorageRawProfile : The storage profile for all VMs in the OVF
package. The value should be raw SPBM
profile. The value will overwrite that in
--defaultStorageProfile. Only applies to VI
targets version 5.5 or newer.
--deploymentOption : Selects what deployment option to use (if
the source OVF package supports multiple
options.)
--disableVerification : Skip validation of signature and
certificate.
-dm/--diskMode : Select target disk format. Supported formats
are: monolithicSparse, monolithicFlat,
twoGbMaxExtentSparse, twoGbMaxExtentFlat,
seSparse (VI target), eagerZeroedThick (VI
target), thin (VI target), thick (VI
target), sparse, and flat
--diskSize : Sets the size of a VM disk in megabytes
using the syntax --diskSize:<VM ID>,<disk
instance ID>=<value>. Only applies to vCloud
targets version 5.5 or newer.
--eula : EULA to be inserted in the first virtual
system or virtual system collection in the
OVF. If the EULA is in a file, use the
option --eula@=filename instead.
--exportDeviceSubtypes : Enables export of resource subtype for
CD/Floppy/Parallel/Serial devices. This can
limit portability as not all device backings
are supported on all hypervisors. The
default is false.
--exportFlags : Specifies one or more export flags to
control what gets exported. The supported
values for VI sources are mac, uuid, and
extraconfig. Supported value for vCloud
sources are preserveIdentity. One or more
options can be provided, separated by
commas.
--extraConfig : Sets an ExtraConfig element for all
VirtualHardwareSections. The syntax is
--extraConfig:<key>=<value>. Applies to vi,
vmx, vapprun, vCloud, ovf, and ova source
locators.
--fencedMode : If a parent network exists on the vCloud
target, this property specifies the
connectivity to the parent. Possible values
are bridged, isolated, and natRouted.
-h /--help : Prints this message.
--hideEula : In OVF probe mode, hides the EULA.
--ipAllocationPolicy : IP allocation policy for a deployed OVF
package.Supported values are: dhcpPolicy,
transientPolicy, fixedPolicy,
fixedAllocatedPolicy.
--ipProtocol : Select what IP protocol to use (IPv4, IPv6).
--lax : Relax OVF specification conformance and
virtual hardware compliance checks. Use only
if you know what you are doing.
--locale : Selects locale for target.
--machineOutput : Output OVF Tool messages in a machine
friendly manner.
--makeDeltaDisks : Build delta disk hierarchy from the given
source locator.
--maxVirtualHardwareVersion : The maximal virtual hardware version to
generate.
--memorySize : Sets the memory size in megabytes of a VM
using the syntax --memorySize:<VM
ID>=<value>. Only applies to vCloud targets
version 5.5 or newer.
-n /--name : Specifies target name (defaults to source
name).
--net : Set a network assignment in the deployed OVF
package. A network assignment is set using
the syntax --net:<OVF name>=<target name>.
If the target is vCloud 5.5 or newer, a
fence mode can also be specified using the
syntax --net:<OVF name>=<target name>,<fence
mode>. Possible fence mode values are:
bridged, isolated, and natRouted.
-nw/--network : Target network for a VI deployment.
--nic : Specifies NIC configuration in a VM using
the syntax --nic:<VM ID>,<index>=<OVF net
name>,<isPrimary>,<ipAddressingMode>,<ipAddress>.
Possible values for ipAddressingMode are:
DHCP, POOL, MANUAL, and NONE. ipAddress is
optional and should only be used when
ipAddressingMode is set to MANUAL. Only
applies to vCloud targets version 5.5 or
newer.
--noDisks : Disable disk conversion.
--noImageFiles : Do not include image files in destination.
--noSSLVerify : Skip SSL verification for VI connections.
--numberOfCpus : Sets the number of CPUs for a VM using the
syntax --numberOfCpus:<VM ID>=<value>. Only
applies to vCloud targets version 5.5 or
newer.
-o /--overwrite : Force overwrites of existing files.
--powerOffSource : Ensures a VM/vApp is powered off before
importing from a VI source.
--powerOffTarget : Ensures a VM/vApp is powered off before
overwriting a VI target.
--powerOn : Powers on a VM/vApp deployed on a VI target.
--privateKey : Sign OVF package with the given private key
(.pem file). The file must contain a private
key and a certificate.
--privateKeyPassword : Password for the private key. Should be used
in conjunction with privateKey if the
private key requires password
authentication. If required and not
specified, the tool will prompt for the
password.
--prop : Set a property in the deployed OVF package.
A property is set using the syntax
--prop:<key>=<value>.
--proxy : Proxy used for HTTP[S] access.
--proxyNTLMAuth : Enable NTLM authentication for proxy.
-q /--quiet : No output to screen except errors.
--schemaValidate : Validate OVF descriptor against OVF schema.
--shaAlgorithm : Select SHA digest algorithm when creating
OVF package. Supported values are SHA1,
SHA256 and SHA512. Default value is SHA256.
--skipManifestCheck : Skip validation of OVF package manifest.
--skipManifestGeneration : Skip generation of OVF package manifest.
--sourcePEM : File path to PEM formatted file used to
verify VI connections.
--sourceSSLThumbprint : SSL fingerprint of SOURCE. OVF Tool verifies
the SSL fingerprint it gets from SOURCE if
the value is set.
-st/--sourceType : Explicitly express that source is OVF, OVA,
VMX, VI, vCloud, ISO, FLP, vApprun
--sslCipherList : Use this to override default OpenSSL ciphers
suite.
--sslVersion : Use this to set preferred TLS/SSL version
for HTTPS connections. The valid values are
as following:
TLSv1_0: Set preferred TLS/SSL version to
TLSv1.0.
TLSv1_1: Set preferred TLS/SSL version to
TLSv1.1.
TLSv1_2: Set preferred TLS/SSL version to
TLSv1.2.
--storageProfile : Sets the storage profile for a VM using the
syntax --storageProfile:<VM ID>=<value>.
Only applies to vCloud targets version 5.5
or newer.
--targetPEM : File path to PEM formatted file used to
verify VI connections.
--targetSSLThumbprint : SSL fingerprint of TARGET. OVF Tool verifies
the SSL fingerprint it gets from TARGET if
the value is set.
-tt/--targetType : Explicitly express that target is OVF, OVA,
VMX, VI, vCloud, ISO, FLP, vApprun
--vCloudTemplate : Create only a vApp template. Default value
is false
--vService : Set a vService assignment in the deployed
OVF package. A vService assignment is set
using the syntax
--vService:<dependencyId>=<providerId>.
--verifyOnly : Do not upload the source but only verify it
against the target host. Applies to VI 4
targets only.
-v /--version : Prints the version of this tool.
--viCpuResource : Specify the CPU resource settings for
VI-locator targets. The syntax is
--viCpuResource=<shares>:<reservation>:<limit>.
--viMemoryResource : Specify the CPU resource settings for
VI-locator targets. The syntax is
--viMemoryResource=<shares>:<reservation>:<limit>.
-vf/--vmFolder : Target VM folder in VI inventory (relative
to datacenter).
For more help, type: --help <topic>, where topics are:
locators : For detailed source and destination locator syntax
examples : For examples of use
config : For syntax of configuration files
debug : For debug purpose
integration : For a list of options primarily used when ovftool is exec'ed
from another tool or shellscript.Использование довольно простое, например я использовал:
$ /Applications/VMware\ OVF\ Tool/ovftool /Users/captain/VirtualBox\ VMs/Windows\ 7/Windows\ 7\ x64.vmwarevm/Windows\ 7\ x64.vmx /Users/captain/VirtualBox\ VMs/Windows\ 7/Windows\ 7/windows_7.ovf
Opening VMX source: /Users/captain/VirtualBox VMs/Windows 7/Windows 7 x64.vmwarevm/Windows 7 x64.vmx
Opening OVF target: windows_7.ovf
Writing OVF package: windows_7.ovf
Disk progress: 5%В папке которой был выполнен экспорт файлов, появятся файлы. Кликаем по файлу с «*.ovf» (у меня это windows_7.ovf):
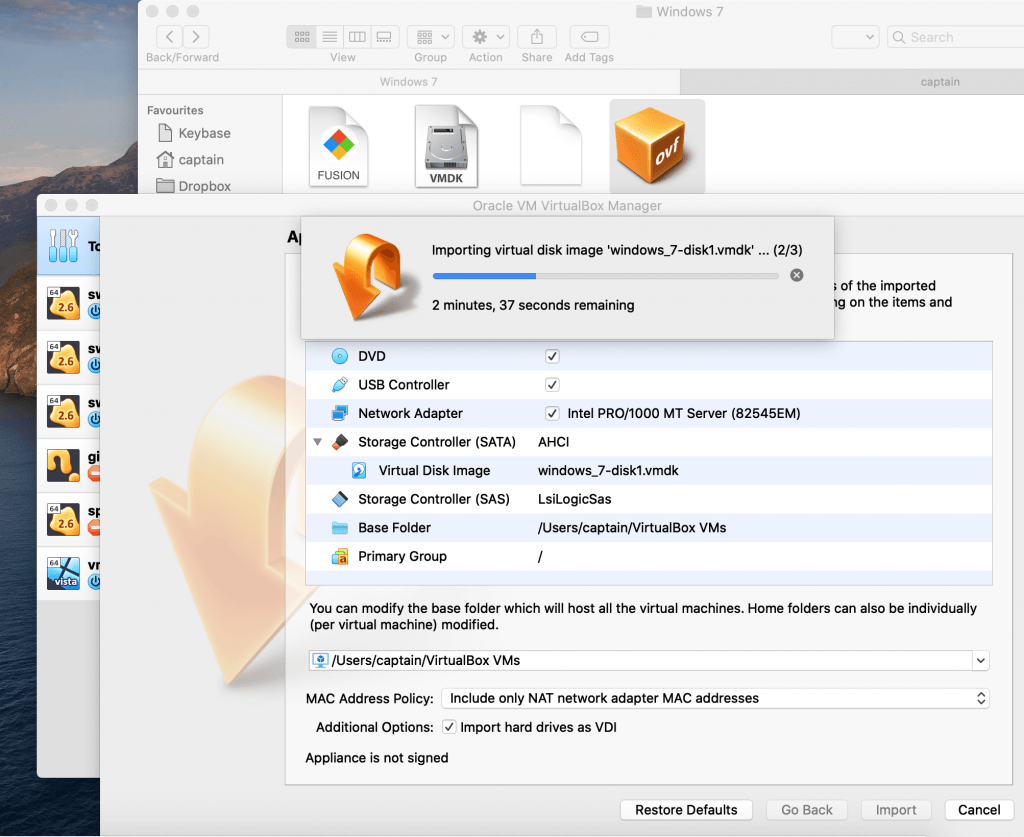
Смотрим что хотим импортить, если что — изменяем и нажимаем на «Import». Импортинг занял 2 минуты у меня для Виндовс 7.
С приходом 64-битной ОС в МакОС, стало сложнее использование старые утилиты. Новые тоже не просто найти бесплатно. По этому, пришлось уйти с VMware…
Конвертация VMware virtual machine -> VirtualBox на Linux
В принципе — все тоже самое что я делал в МакОС, только нужно скачать бинарный файл для Linux-а. Если у кого-то возникнут трудность — смогу помочь! Пишите в комментариях возникшие ошибки и при первой возможности — отпишусь.
Вот и все, статья «Конвертация VMware virtual machine -> VirtualBox в Unix/Linux» завершена.